
In our recently published research, “Alignment of marketing strategies in the pharmaceutical supply chain through a system dynamics simulation modelling”, in the International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Healthcare Marketing, we investigated how alignment of marketing strategies can improve the pharmaceutical supply chain performance.
Through a system dynamics simulation study, this research examines how aligning marketing strategies across the pharmaceutical supply chain — from manufacturers to distributors to pharmacies — can improve both efficiency and responsiveness in a sector vital to public health and highly sensitive to external shocks.
A few highlights from the paper
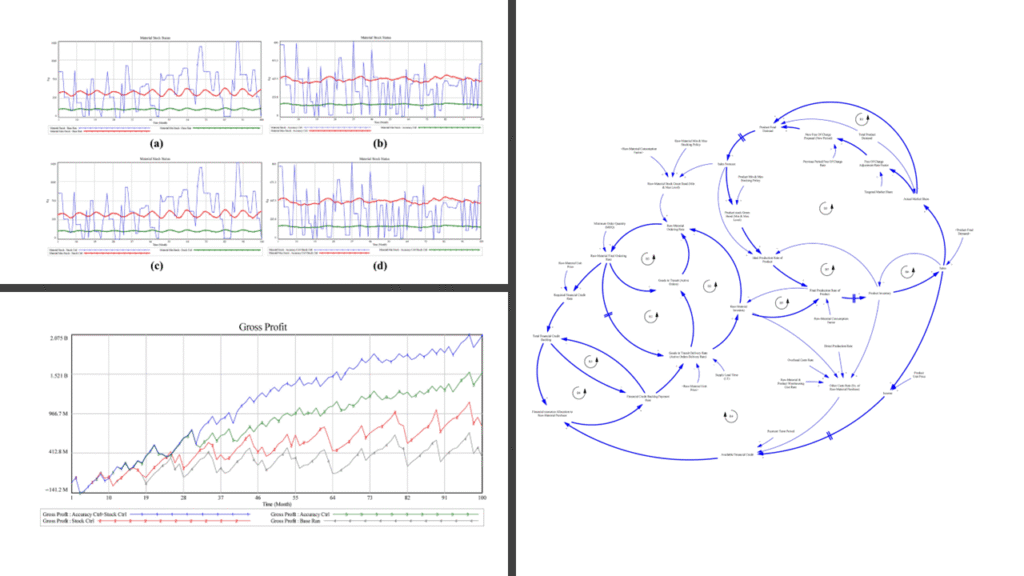
- Aligning Marketing Strategies with Inventory Dynamics – Announcing and adjusting marketing strategies, free-of-charge (FOC) promotions here, based on demand forecasts and inventory levels, reduces the bullwhip effect, lowers costs, and improves profitability across the pharmaceutical supply chain.
- Integration and Digital Transformation – Stronger coordination between marketing, retail, and production teams, supported by advanced forecasting, AI, blockchain, and integrated information systems, enhances flexibility, reduces stock fluctuations, and ensures timely, equitable access to medicines.
- Balancing Short- vs. Long-Term Outcomes – While aggressive promotions can temporarily boost market share, sustainable strategies that integrate demand forecasting and adaptive marketing policies lead to more resilient supply chains, higher net income, and stable medicine availability.
Why it matters
Pharmaceutical supply chains are highly sensitive to demand fluctuations, long lead times, and competitive pressures. Misaligned marketing strategies—such as poorly timed free-of-charge promotions—can amplify the bullwhip effect, inflate costs, and create stockouts. Our findings show that aligning marketing decisions with demand forecasts and inventory realities, supported by digital technologies, not only reduces inefficiencies but also strengthens resilience. This alignment ensures medicines remain affordable, accessible, and delivered on time, benefiting both firms and patients while improving long-term equity in healthcare delivery.
Who benefits
- Pharmaceutical companies and supply chain managers – to reduce costs, minimise the bullwhip effect, and improve profitability.
- Policymakers and regulators – to strengthen the pharmaceutical supply chain resilience, improve equity, and support affordable medicine delivery.
- Researchers – to advance modelling, forecasting, and digital integration in pharmaceutical logistics.
I’m grateful to my collaborators, Ehsan Gilani, Seyedehfatemeh Golrizgashti, Alireza Irajpour, and Sondoss Elsawah, and the reviewers for their constructive feedback. If you’re interested in discussing its implications for your organisation or context, I’d love to connect and chat.
Access the paper
👉 Read the full paper here:
https://doi.org/10.1108/IJPHM-10-2024-0117
Full Abstract
Purpose
This study aims to investigate the impact of retailer–supplier partnerships (RSP), a crucial type of supply chain-related strategic alliance, in mitigating the bullwhip effect (BWE) caused by an unintegrated, sales-focused management approach among pharmaceutical supply chain (PSC) partners. It explores how integrated management strategies in PSC, using free-of-charge (FOC) rewards as a marketing promotion tool, can optimise capillary distribution networks.
Design/methodology/approach
A system dynamics (SD) simulation model is developed to investigate the effectiveness of RSPs in enhancing the overall PSC performance. To do so, a PSC case study is used to conceptualise and develop the simulation model, with FOC used as the primary marketing promotion tool in capillary network sales. The model evaluates the impacts on PSC metrics, including sales loss, income, production costs and raw material purchase costs.
Findings
Improvement scenarios are proposed to optimise the market promotion policies, achieving sales targets while stabilising production, procurement and financial operations. The simulation results demonstrate significant improvements in decreasing sales loss, production operational costs and raw material purchase costs and increasing income and profitability. In addition, errors in raw material and product stocking decreased, and the market share increased notably, demonstrating the benefits of a coordinated PSC.
Originality/value
This study extends existing research by presenting an SD model on RSP within PSCs, emphasising the often-overlooked marketing component in integrated PSC planning. It provides insights into how strategic alliances and integrated management approaches can alleviate common PSC challenges, such as BWE.
Keywords
Supply chain, Retailer–supplier partnerships, Pharma industry, System dynamics, Marketing promotion policies

Let’s learn Systems Modelling together!
I share useful information about Systems Modelling here weekly.